Numerical value, notation, and units
The speed of light in vacuum is usually denoted by a lowercase c, for "constant" or the Latin celeritas (meaning "swiftness, celerity"). In 1856, Wilhelm Eduard Weber and Rudolf Kohlrausch had used c for a different constant that was later shown to equal √2 times the speed of light in vacuum. Historically, the symbol V was used as an alternative symbol for the speed of light, introduced by James Clerk Maxwell in 1865. In 1894, Paul Drude redefined c with its modern meaning. Einstein used V in his original German-language papers on special relativity in 1905, but in 1907 he switched to c, which by then had become the standard symbol for the speed of light.
Sometimes c is used for the speed of waves in any material medium, and c0 for the speed of light in vacuum. This subscripted notation, which is endorsed in official SI literature, has the same form as other related constants: namely, μ0 for the vacuum permeability or magnetic constant, ε0 for the vacuum permittivity or electric constant, and Z0 for the impedance of free space. This article uses c exclusively for the speed of light in vacuum.
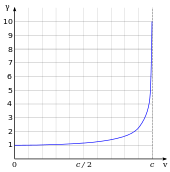
Since 1983, the metre has been defined in the International System of Units (SI) as the distance light travels in vacuum in 1⁄299792458 of a second. This definition fixes the speed of light in vacuum at exactly 299792458 m/s. As a dimensional physical constant, the numerical value of c is different for different unit systems.Note In branches of physics in which c appears often, such as in relativity, it is common to use systems of natural units of measurement or the geometrized unit system where c = 1. Using these units, c does not appear explicitly because multiplication or division by 1 does not affect the result.
Comments
Post a Comment